Abstract
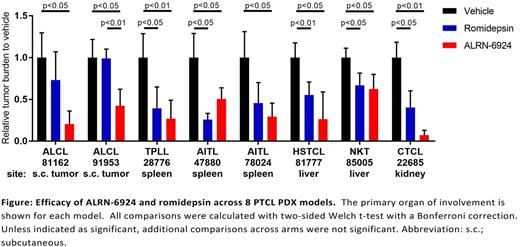
T-cell lymphomas (TCL) are a heterogeneous group of non-Hodgkin lymphomas with poor outcomes. Biological heterogeneity across TCLs has hampered the development of targeted therapies. Thus, we sought to identify common vulnerabilities that could be targeted across multiple TCL subtypes. We performed transcriptome and exome sequencing of 21 TCL cell lines and 8 TCL patient-derived xenografts (PDX), and a genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 pooled screening in 7 TCL lines. Sequencing identified multiple genomic alterations of clinical significance and disease-specific recurrence, like activating JAK1 and STAT3 mutations in cell lines and a PDX-model of anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) or mutations of TET2, DNMT3A and RHOA in PDX-models of angioimmunoblastic TCL (AITL). Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of transcriptomes identified disease-specific gene-expression profiles across cell lines and PDX models. Ranking the genetic vulnerabilities of the CRISPR-Cas9 screen by z-score and recurrence across multiple cell lines, we identified both previously defined (e.g. IRF4) and novel vulnerabilities (e.g. PTPN2) within multiple TCL subtypes. The most consistent dependence in TP53- wild-type (WT) lines was the E3 ubiquitin ligase MDM2, which polyubiquitinates and targets p53 for degradation. Multiple TCL lines harbored copy number gains or amplifications of MDM2 and/or MDMX that correlated with high transcript levels. To address the therapeutic potential for targeting MDMX/MDM2 in TCL we tested ALRN-6924, a p53-derived stapled peptide that inhibits both MDMX and MDM2, and that is currently in multicenter phase I/Ib and phase II trials. ALRN-6924 was recently shown to induce objective responses in a variety of cancers as a single agent in phase 1 dose-escalation (Meric-Bernstam, F. et al, ASCO 2017). Our results showed that ALRN-6924 potently induced G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cell death in WT TP53 TCL lines (n=8; IC50 100 nm-1 µM) while inducing expression of p21 and Annexin V. ALRN-6924 was inactive in TP53 -mutant lines (n=11; IC50 > 5 µM). Next, we performed a phase II-like trial in eight WT TP53 PDXs: hepatosplenic (HS-TCL), cutaneous (CTCL), NK/T, AITL (n=2), T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia (TPLL) and Alk+ ALCL (n=2). At the time of extensive lymphoma engraftment (e.g. >20% splenic involvement), mice were randomized to treatment with vehicle, ALRN-6924 or the 2nd line standard-of-care agent Romidepsin (n=3/arm/model) on days 1, 4 and 7, and sacrificed on day 8. ALRN-6924 had a favorable safety profile and significantly reduced tumor burden compared to vehicle in all 8 models, with superior efficacy to Romidepsin in the majority of models (Figure). Residual tumor cells collected from ALRN-6924-treated mice consistently had increased AAD/Annexin V staining and p21 induction, consistent with on-target p53 activation and apoptosis.
In summary, we identified MDM2/MDMX as a targetable vulnerability that is effectively targeted by the stapled peptide ALRN-6924 in TP53 WT TCLs with promising activity across multiple subtypes, supporting further clinical development of ALRN-6924 in TCL for patients requiring 2nd or frontline treatment. A Phase IIa clinical trial of ALRN-6924 in PTCL patients is currently enrolling (NCT02264613).
Horwitz: Millenium/Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; HUYA: Consultancy; Forty-Seven: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kyowa-Hakka-Kirin: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Mundipharma: Consultancy; ADCT Therapeutics: Research Funding; Aileron Therapeutics: Research Funding; Infinity/Verastem: Consultancy, Research Funding. Santiago: Aileron: Employment. Ren: Aileron: Employment. Guerlavais: Aileron: Employment. Annis: Aileron: Employment. Aivado: Aileron: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal